Recently, the Russian State Duma approved changes to the Russian Tax Code. These measures are part of a government response program, “ultra-low tax regime,” with the aim of stimulating the growth and revenues of Russian IT companies. One of the consequences of this change in the law is that IT companies are now eligible for several tax benefits.
The amendments primarily cover tax rates and residency issues.
Here’s a closer look at each and their impact.
Changes to the Profits Tax
One of the most newsworthy items to come out of this new law is that IT companies will be able to pay Profits Tax at the rate of 3% instead of 20%. This is a significant drop. All the tax will transfer to the federal budget, with zero applied to the regional budget.
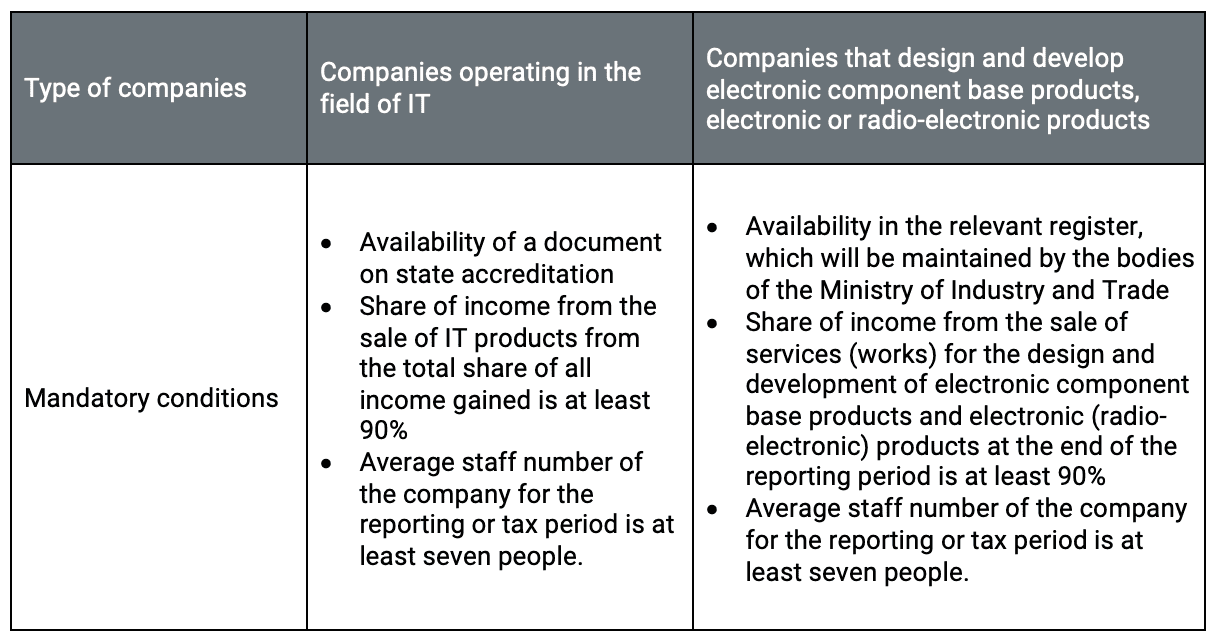
Who is eligible for this reduced tax rate?
There are two categories of companies who will qualify for this new rate:
If these conditions are not met, the tax payable will be assessed at the general rate of 20%.
Changes to insurance premiums
Those organizations with the right to reduced income tax rates also qualify to pay reduced insurance premiums in the following types of insurance:
- Compulsory pension insurance (CPI) – 6%
- Compulsory health insurance (CHI) – 0.1%
- Compulsory social insurance (CSI) – 1.5%
Companies wishing to apply for reduced contribution rates must meet similar conditions as those provided for the reduced income tax rates.
Changes to VAT rates
Currently, the realization of exclusive rights (and rights under the licensing agreement) to any software is not subject to VAT. However, from January 2021, realization operations will be exempt from VAT per the following:
- exclusive rights to computer programs and databases included in the unified register
- rights to use these programs and databases.
Rights to use may be transferred by entering into a licensing agreement, and by providing remote access to programs and databases via the Internet, including updates and additional functionality.
The exemption cannot be waived.
However, it should be noted that the VAT exemption will not be applied to the transfer of rights to use computer programs and databases, if these rights consist in obtaining the ability to:
- distribute advertising on the Internet and gain access to it
- post offers on the Internet for the purchase or sale of goods, works, services, and property rights
- search for information about potential buyers and sellers or conduct transactions.
The exclusive rights to inventions, utility models, industrial designs, know-how, and the right to use these intellectual property results will remain exempt from VAT.
Changes to tax residency rules
If an individual has been in the Russian Federation in the period from 90 to 182 calendar days inclusively during 2020 (from January 1 to December 31), he or she can obtain or retain the status of a tax resident of the Russian Federation.
To obtain this status, an individual should apply to the relevant tax authority. It is necessary to specify the employee’s full name and taxpayer ID number (Russian acronym – INN) in the application. The timeframe for submitting an application is not later than April 30 of the following year.
Remember, according to the Russian Federation Tax Code, individuals who reside in Russia for at least 183 calendar days within a period of 12 consecutive months are recognized as tax residents. The income of such persons is subject to personal income tax at the rate of 13%, but at the date from when this resident status is lost, the tax will have to be paid at an increased rate of 30%.
To keep up to date with other legislative updates from across the globe, why not take a look at some of our other blogs.
Want to learn about Immedis, our global payroll platform, and hear more from our knowledgeable team? Get in touch below:
Back to all country updates